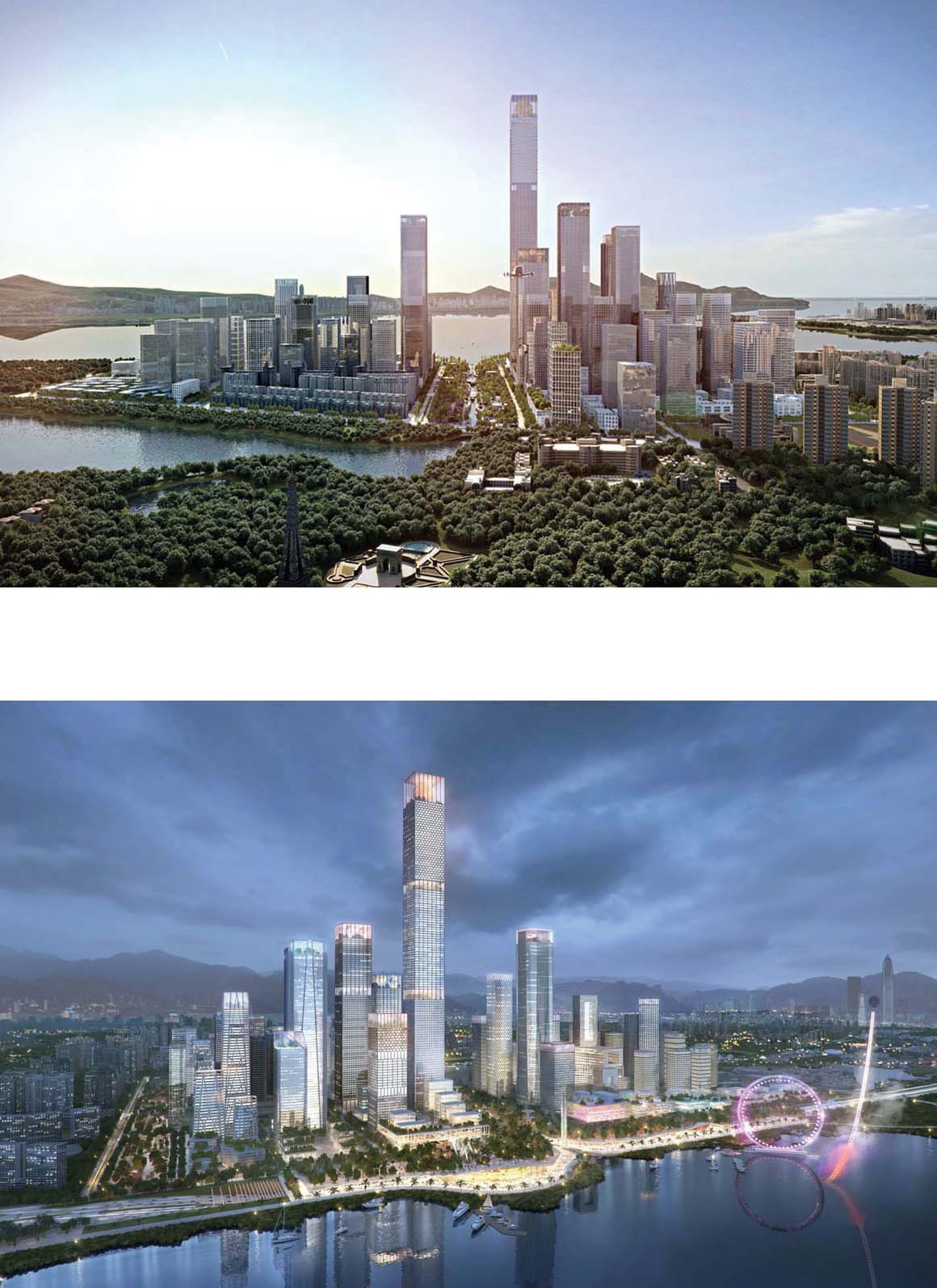
From 15 participants, three winners have been selected to collaborate in the design of a new 5.5-million-m² district that will become the new center of Shenzhen, a polycentric megacity of 20 million people. Henning Larsen is the only foreign team among the winners.
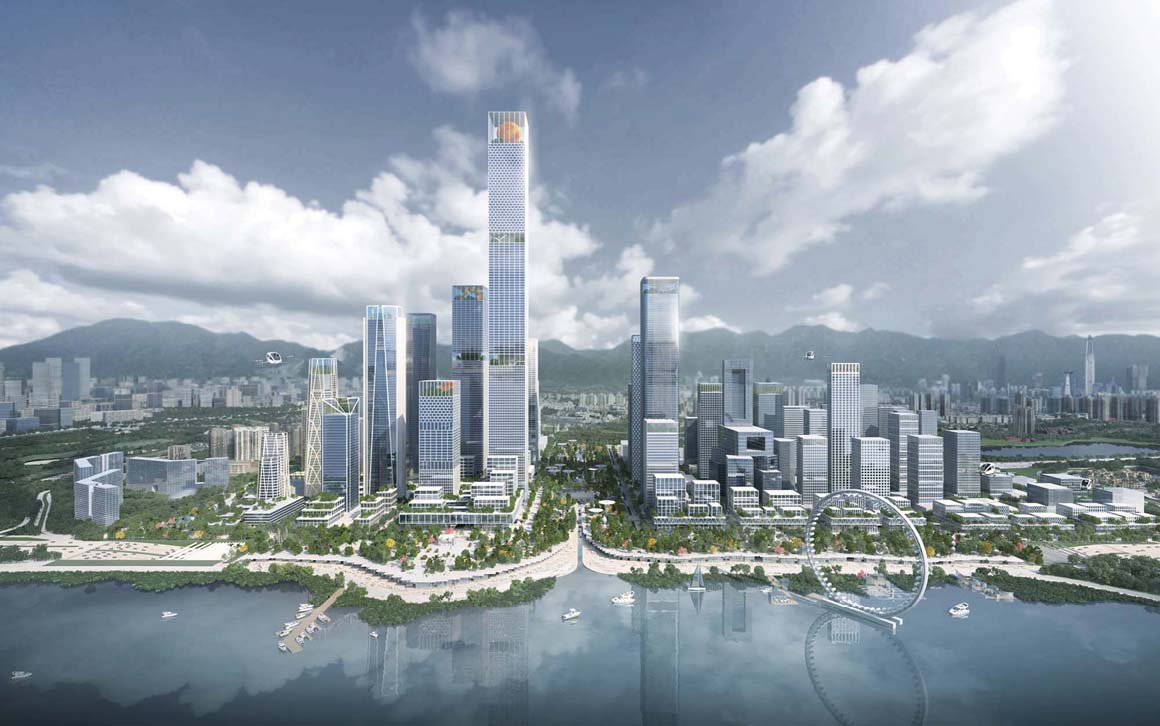
Shenzhen Bay Headquarters City is poised to become the lightning rod for development in Shenzhen and the Greater Bay Area, the largest bay economy in the world.
To establish Shenzhen as the heart of the Greater Bay Area, Henning Larsen envisioned an ambitious masterplan that shifts the paradigms of Chinese urban planning and sets the standard for the green, sustainable and livable city of the Future China.

Making Shenzhen a Waterfront city
The design aims to make Shenzhen the waterfront city it should always have been. To create an attractive waterfront, the architects brought commercial and cultural facilities meters away from the seashore, so that citizens will finally be able to enjoy the atmosphere of Shenzhen Bay in an activated urban environment such as Sydney, Singapore or Copenhagen.
A Pedestrian City Center
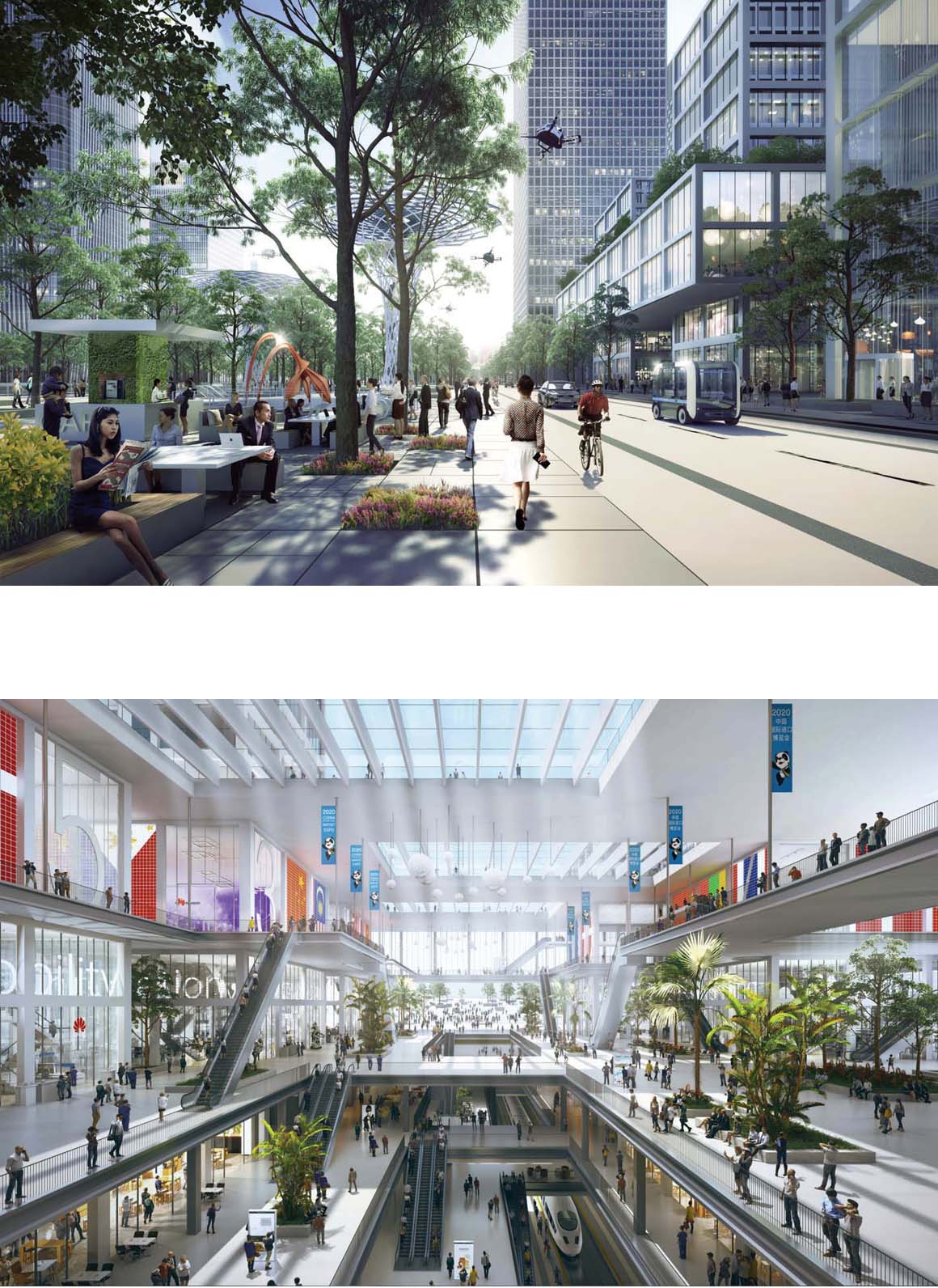
Henning Larsen’s design aims to create a pedestrian urban realm; cars are relegated to an extensive underground network of highways, roads and parking.
All the basement levels of the district are interconnected in a network of retail arcades and sunken plazas, replacing the need for outsized shopping malls above ground.
In lieu of the massive shopping malls traditionally sitting beneath tall buildings, Henning Larsen proposes a porous urban fabric composed of smaller buildings sitting in between the towers. At eye level, this urban typology offers a human scale with narrow alleys and small piazzas.
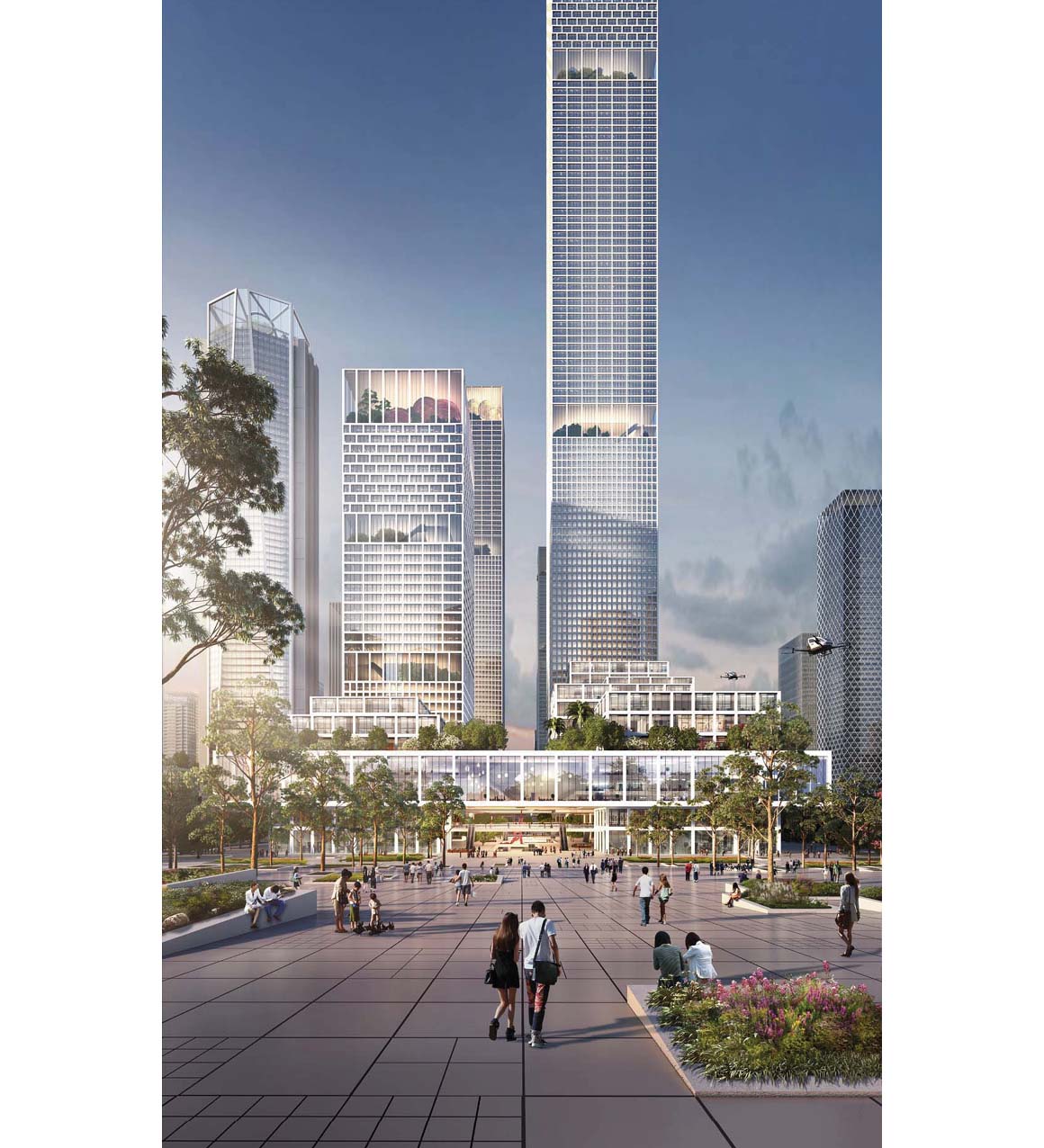


A Cooler Part of Town
This porous urban fabric also allows effective urban ventilation by making use of the sea breeze, which contributes to cooling the district significantly in the punishing heatwaves of the summer. Other measures to cool the district include planting 10,000 trees, roof gardens and whitewashed streets.
“We know by experience that these initiatives can reduce the heat within the district by 5-8 degrees compared to the surrounding city. The added comfort level will encourage citizens to use the public realm,” explains Claude Godefroy, Partner and Design Director of Henning Larsen’s Hong Kong office.
A Shared City
The sharing economy is increasingly changing workspaces and challenging the dogmas of what modern cities should be. The Shenzhen Bay masterplan offers a range of shared working spaces in both dedicated buildings and integrated into the public realm. The dedicated co-working buildings are spread out in the masterplan and offer independent access, larger floorplates, internal atriums, and access to amenities such as coffee shops, gyms, and shared meeting rooms.