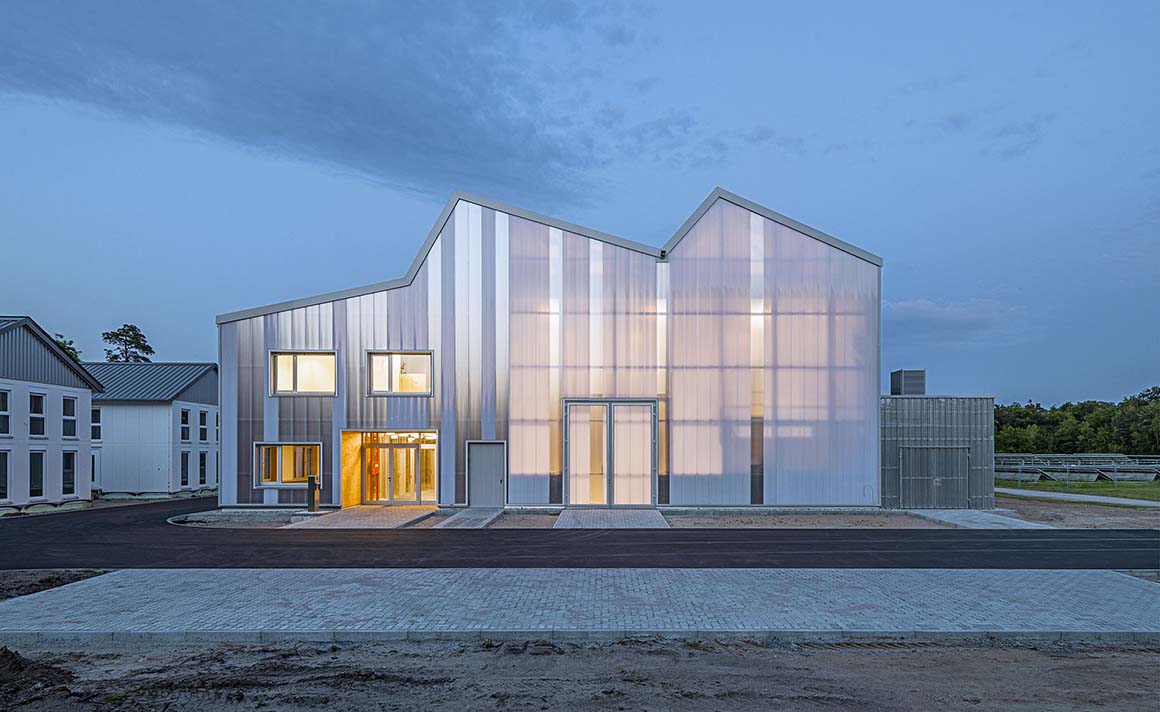
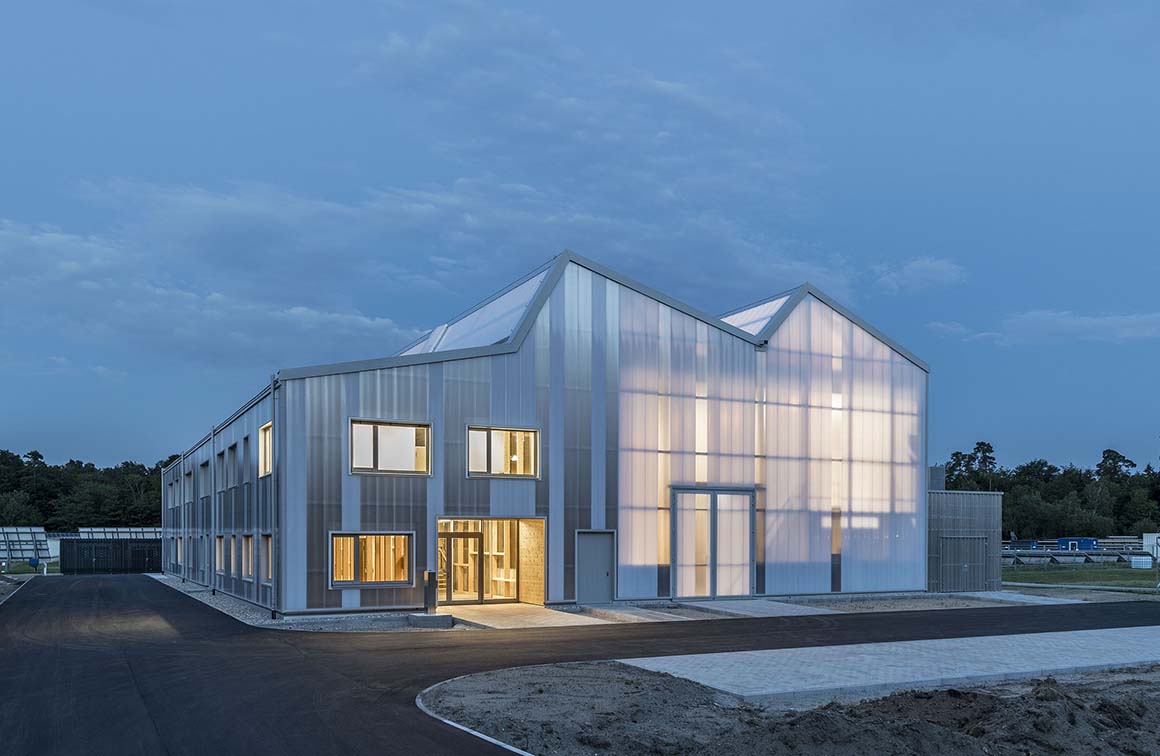
Translucent polycarbonate walled and saw-tooth topped

The Energy Lab 2.0 at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) is an intelligent platform set up to explore the interplay of components in the energy systems of the future and in particular to speed up energy transition in Germany, through the integration of renewable energy in the production of electricity. Electrical, thermal and chemical energy flows, as well as new information and communication technologies, are combined in a cluster of facilities. The project partners are the Helmholtz Centers, the National Aeronautics and Space Research Center of the Federal Republic of Germany (DLR) and Forschungszentrum Jülich (FZJ).
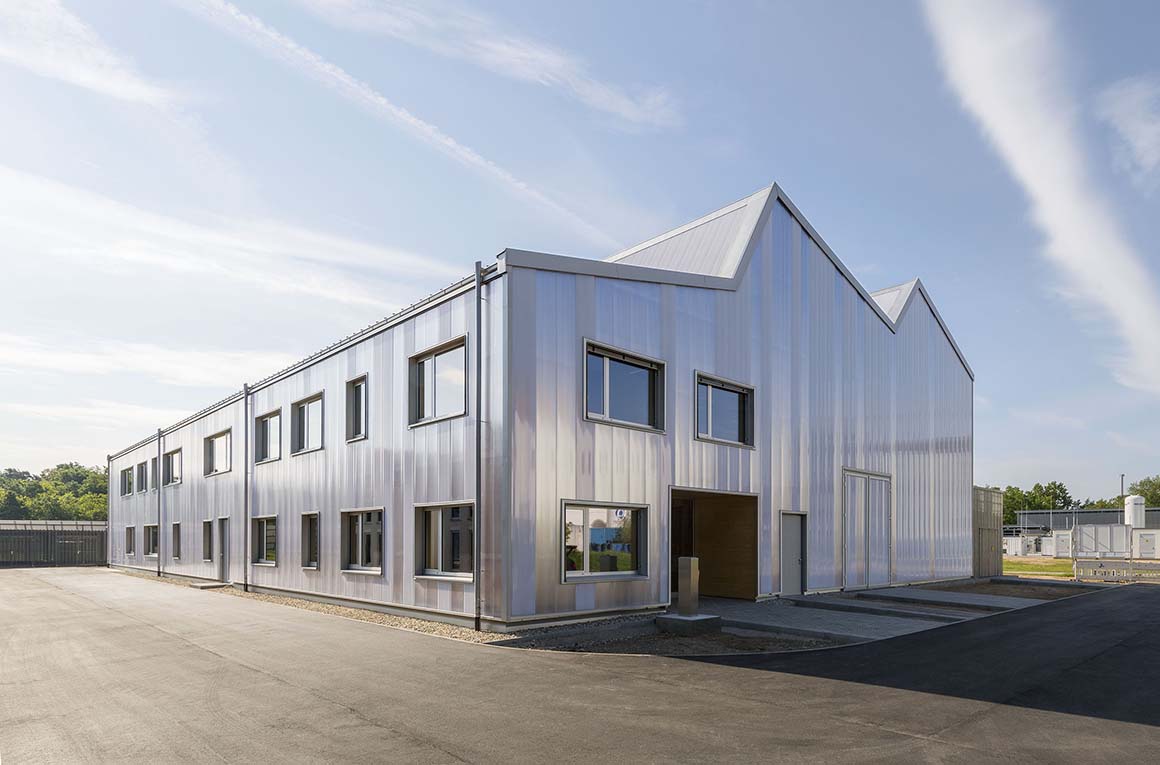
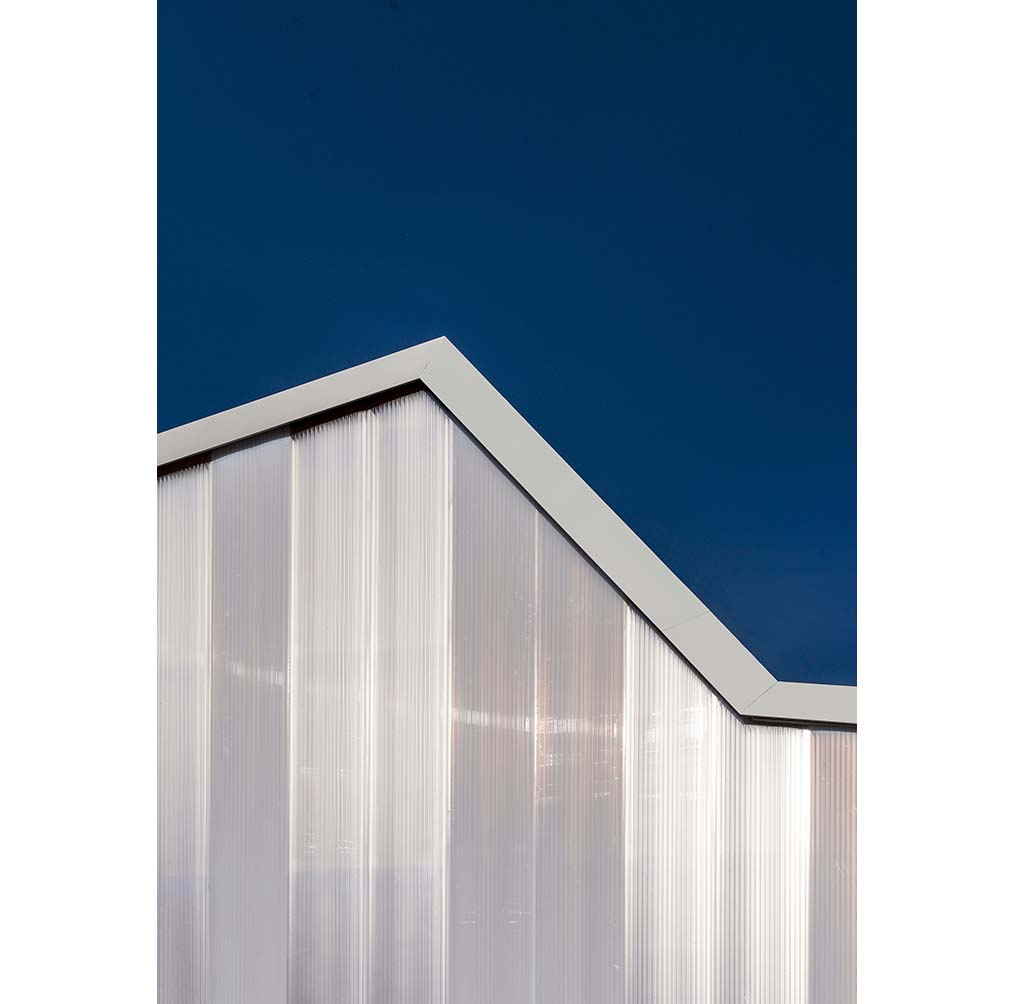


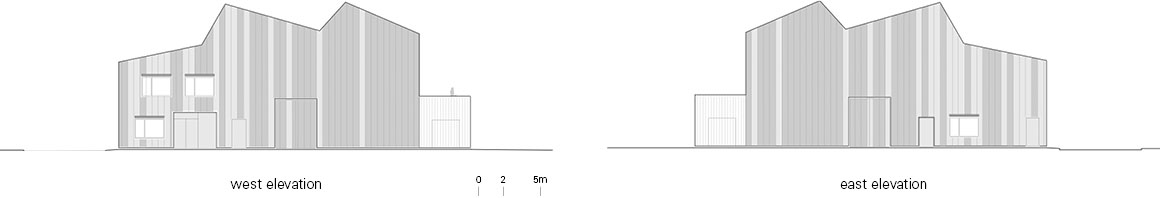

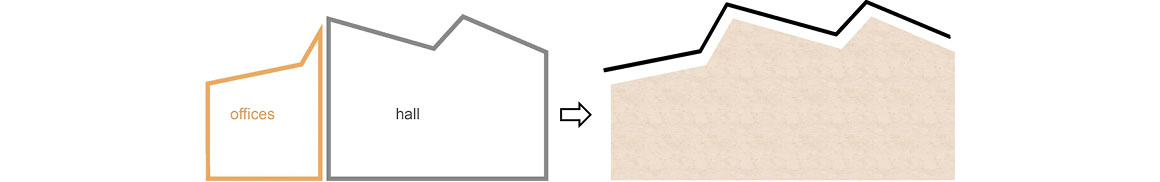
The new construction of Building 668, on a site formerly used for experiments with solar energy in the north of the campus, provides an attractive, high quality and flexible location for this research. The detached building has the appearance of a homogenous unit with a translucent polycarbonate building envelope that allows the wooden construction on the interior to shimmer through, and accommodates an ample, column-free test hall as well as a two-story office wing.
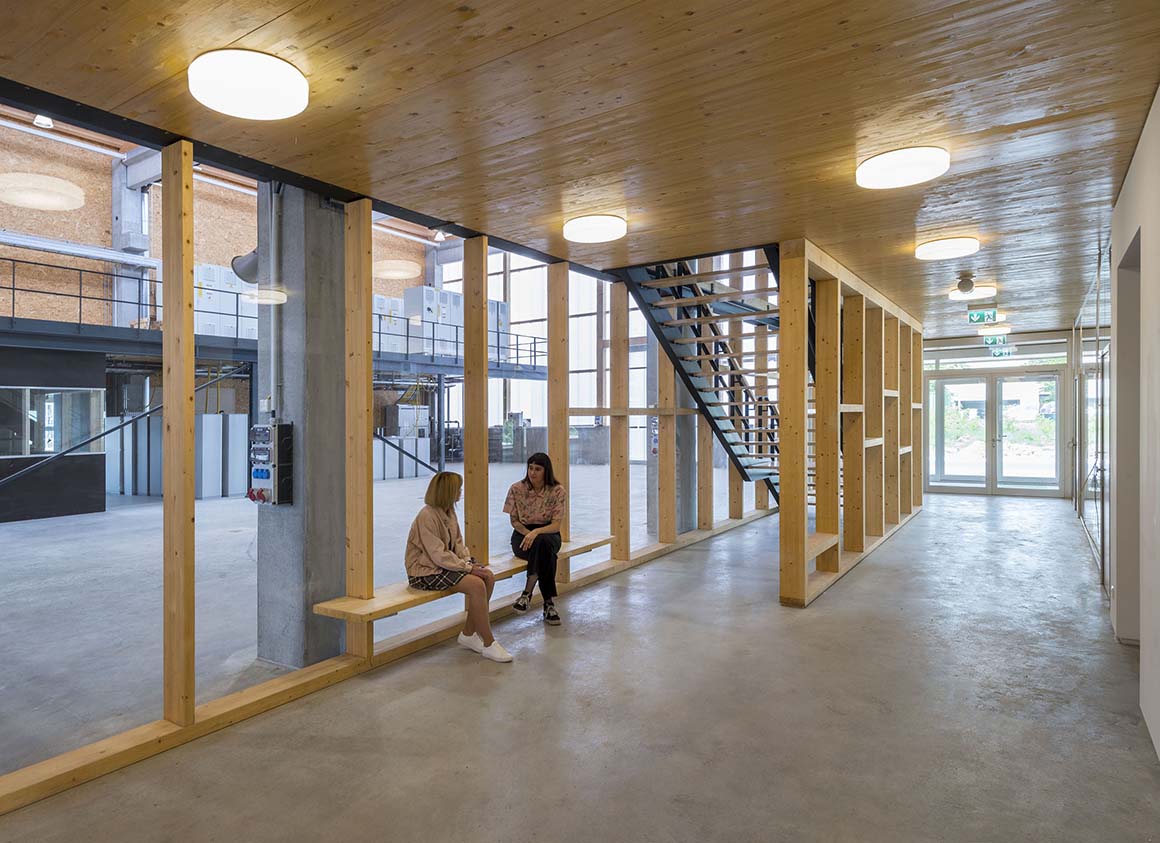
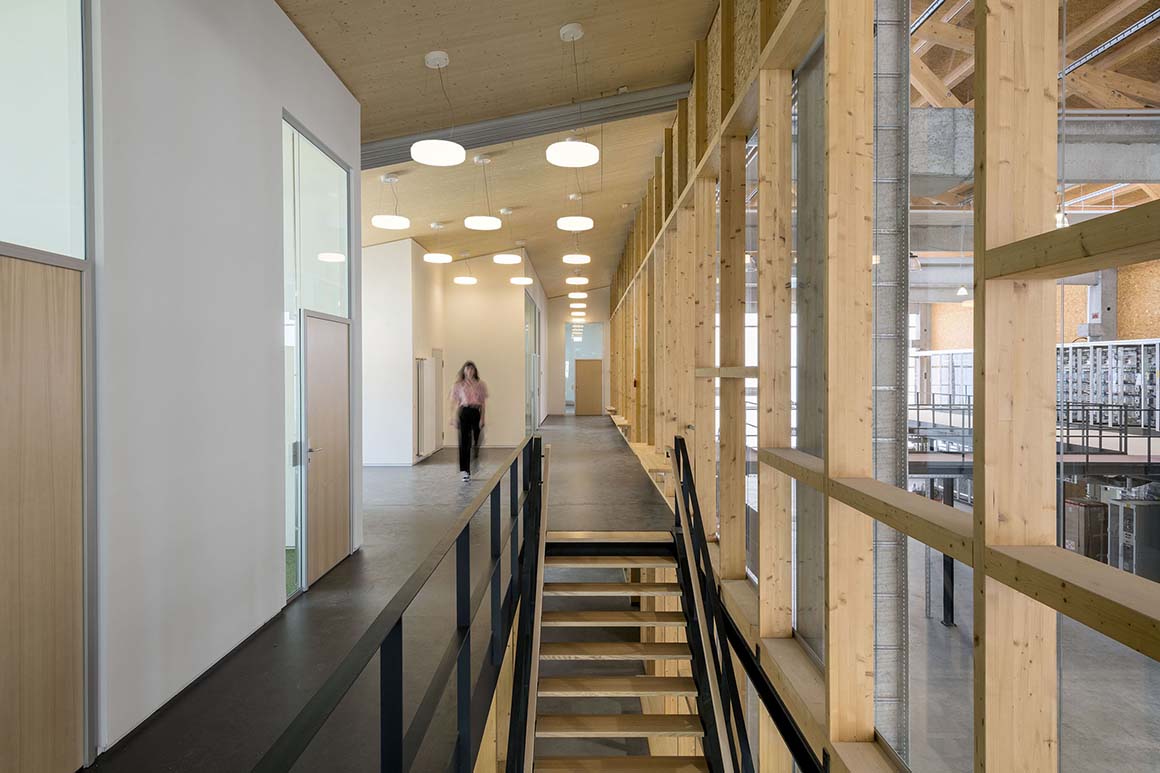
The main approach is from the west via a glass vestibule in the central zone of access, which leads between the offices and the hall alongside a lightweight glass wall, into the building, allowing generous views between these building sections. The right side opens up onto a hall, while the office spaces are aligned on the left. The control station, the test preparation area, the meeting rooms and the auxiliary rooms are also located here. In the building center, a stairway and elevator lead to the upper story, where additional office and preparation rooms are located, as well as a small staff kitchen with seating. The rooms allocated to the test areas are adjacent to the atrium and provide direct views into this open space.
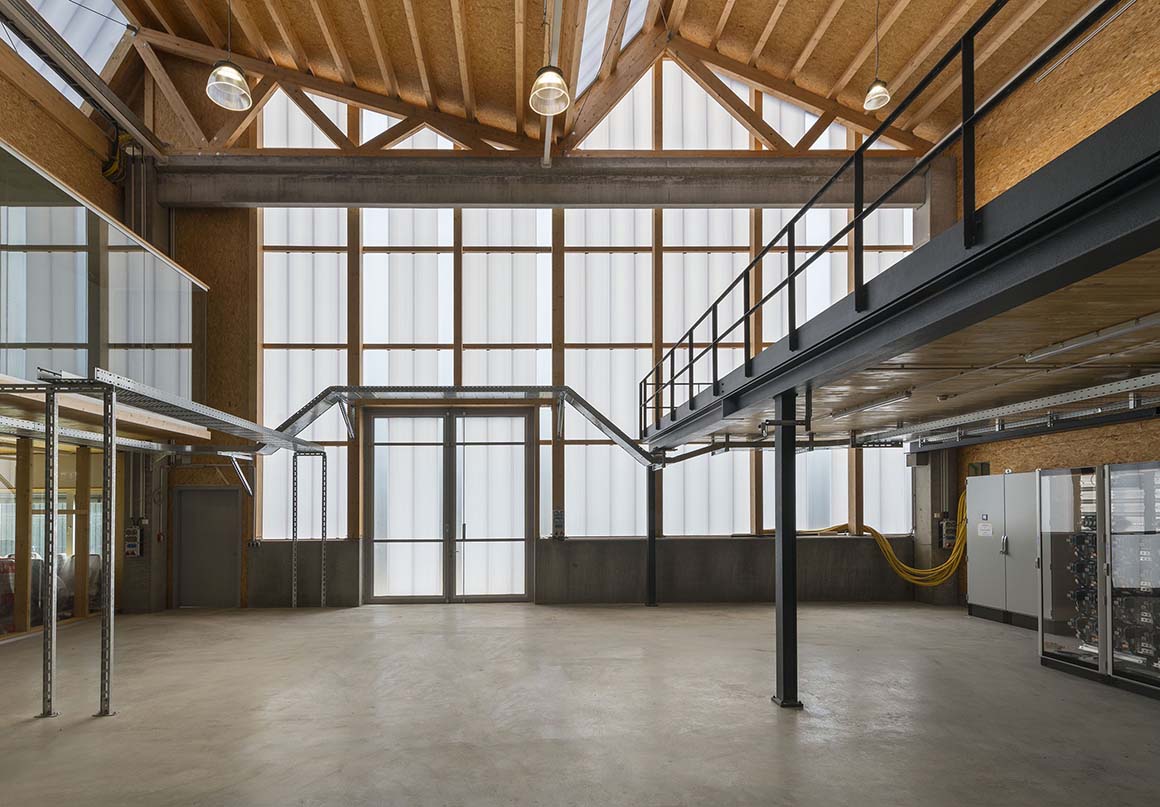
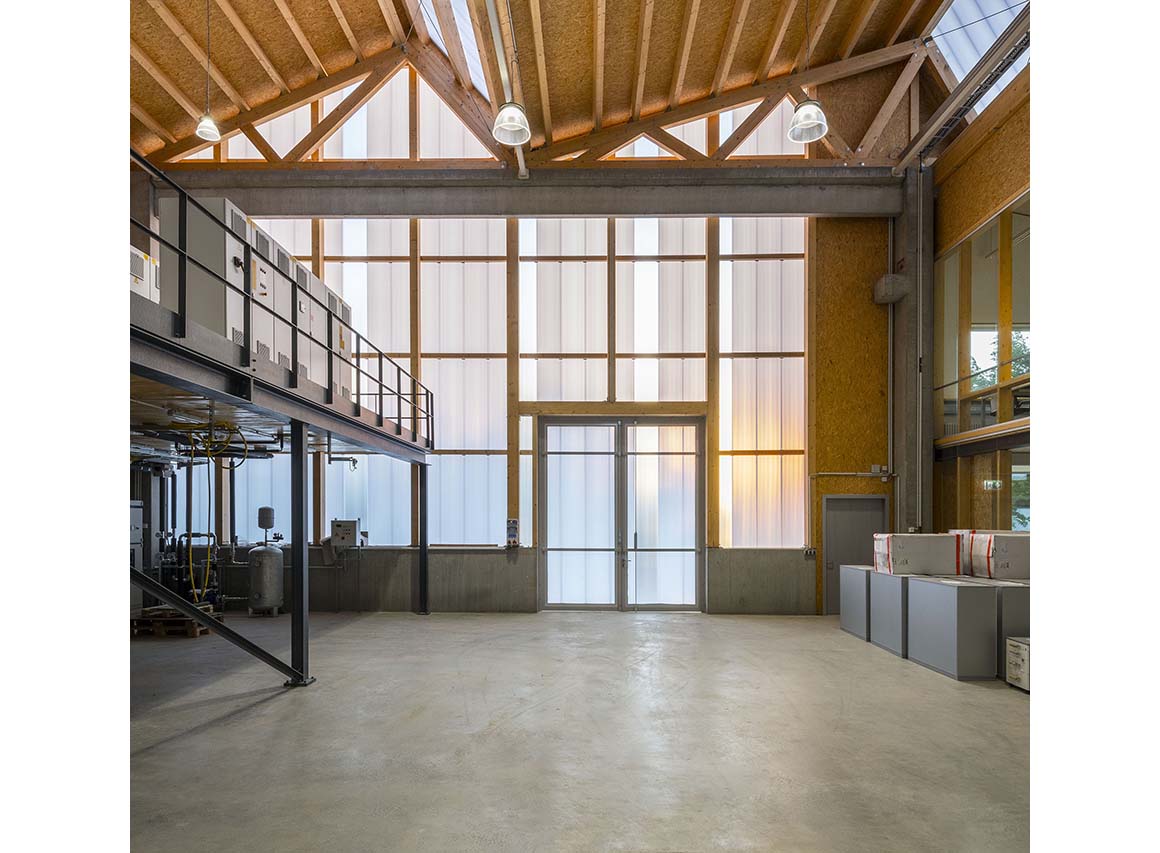
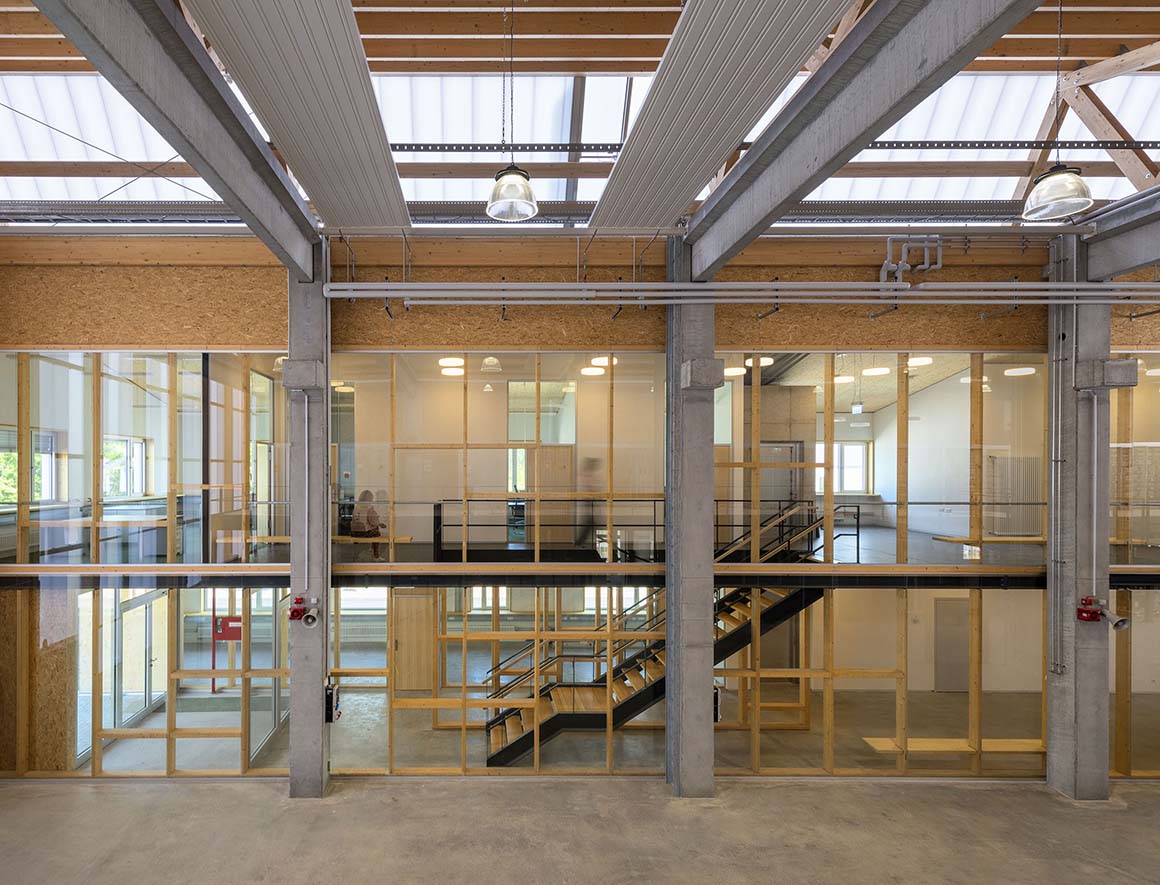

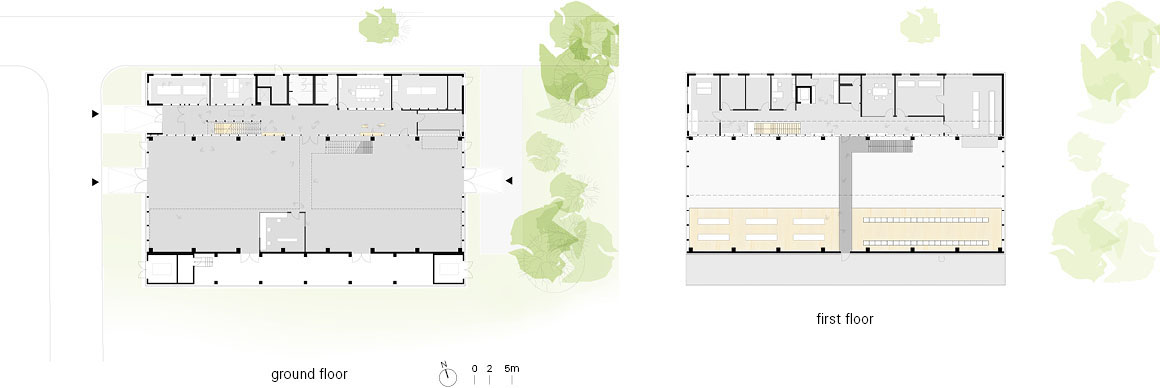


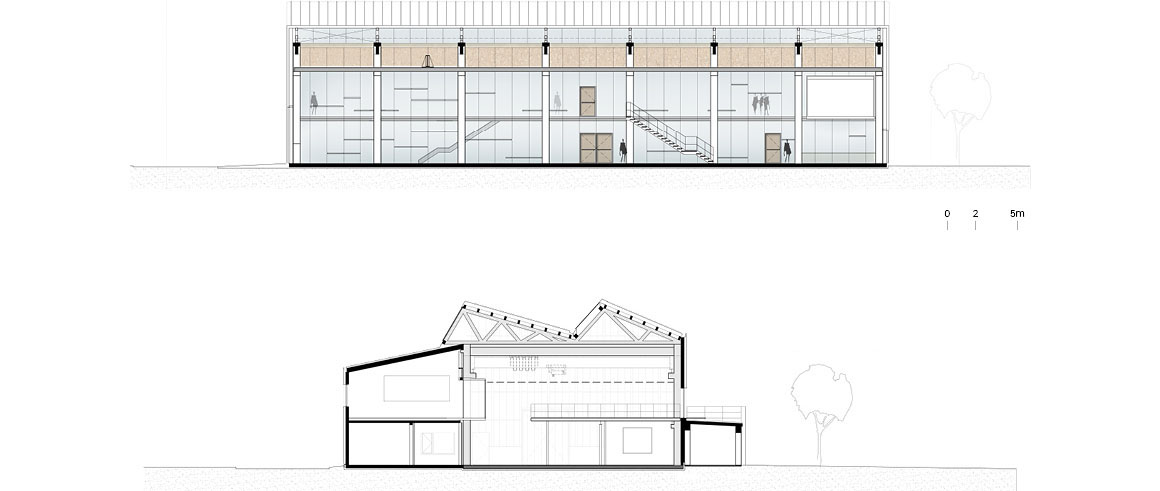



The test hall accommodates the areas called “Power-Hardware in the Loop” (PHIL) and “Smart Energy System Control Laboratory” (SESCL) as well as assembly areas for tests. The hall and the saw-tooth roof are generously clad with translucent polycarbonate plates, which allow a consistent amount of daylight to enter the entire test area. Adjacent assembly areas for technical construction elements with large thermal loads are not part of the energy system of the building envelope but instead, with their slatted façade, ensure consistent heat removal and ventilation of the construction elements.
The material of the hall incorporates references to the neighboring buildings with their industrial character. Window openings set in specific places in the office façade enable a selective illumination of the interior spaces with their unobtrusive design. While here wood and simple glass façades are the dominant design element, the hall is characterized by the polycarbonate façade and the wooden construction of the saw-tooth roof.

Project: KIT Energy Lab 2.0 / Location: Hermann-von-Helmholtz-Platz 1, 76344 Eggenstein-Leopoldshafen, Germany / Architect: Behnisch Architekten / Partner: Jörg Usinger / Project leader: Kari Silloway (from 1.17), Nevyana Tomeva (to 12.16) / Engineer: Norconsult / Client: Facility Management KIT / Gross area: 1,730m² / Net floor area: 1,238m² / Volume: 1,730m3 / Number of workplaces: 25 / Number of floors above ground: 2 / Planning and construction: 2015~2019 / Photograph: ©Adam Mørk (courtesy of the architect)